The principal use of ball screw assemblies is to mechanically convert rotary motion into linear motion. They can serve for table positioning or linear actuator applications. A rotary encoder, when attached to the end of the ball screw shaft or the drive motor, provides feedback used to determine linear speed, direction, rate and position.
Mechanically, both shaft and thru-bore encoders can be applied to ball screws, but hollow bore or thru-bore encoders tend to be used more frequently.
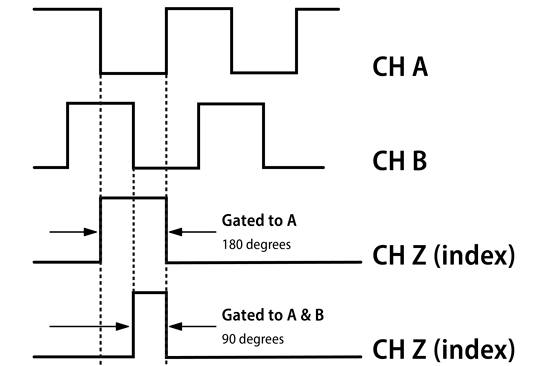
Electrically, variables such as resolution, output type, channels, voltage, etc., can be specified to meet the individual application requirements. Due to the reciprocating motion typical of ball screw assemblies, quadrature output is required to determine direction of travel. Additionally, an index pulse should be specified to ensure the ability to find a home position. For situations where position is needed during power-off scenarios without cycling back to a known home position, select a multi-turn absolute encoder.
Environmental considerations are important when specifying your encoder. Take into account the encoder's exposure to liquids, fine particulates, extreme temperatures, and washdown requirements. An IP66 or IP67 seal protects against moisture ingress, while a stainless steel or polymer composite housing to mitigate the effects of harsh cleaning chemicals and solvents.
Examples of Ball Screw Positioning
- Machine tool placement
- Industrial lifting jack
- Printer carriage positioning