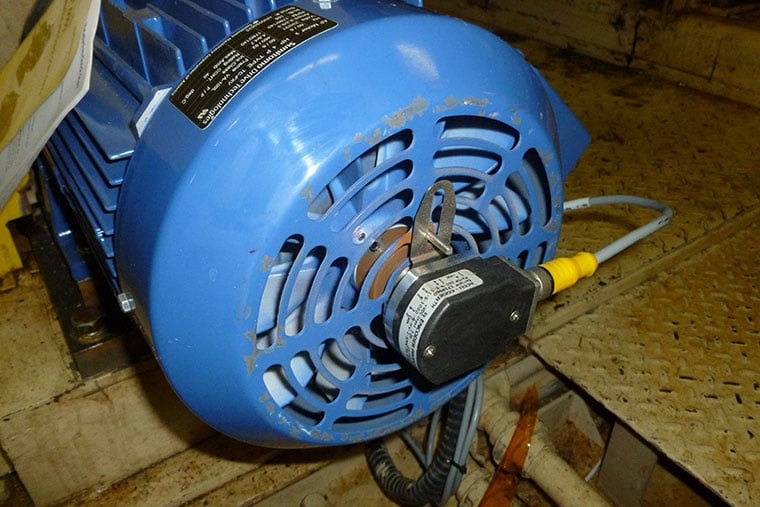
An optical encoder is a type of motion sensing device that uses light shone through a coded disk to track the movement of a shaft. The encoder provides feedback based on the interruption of light.
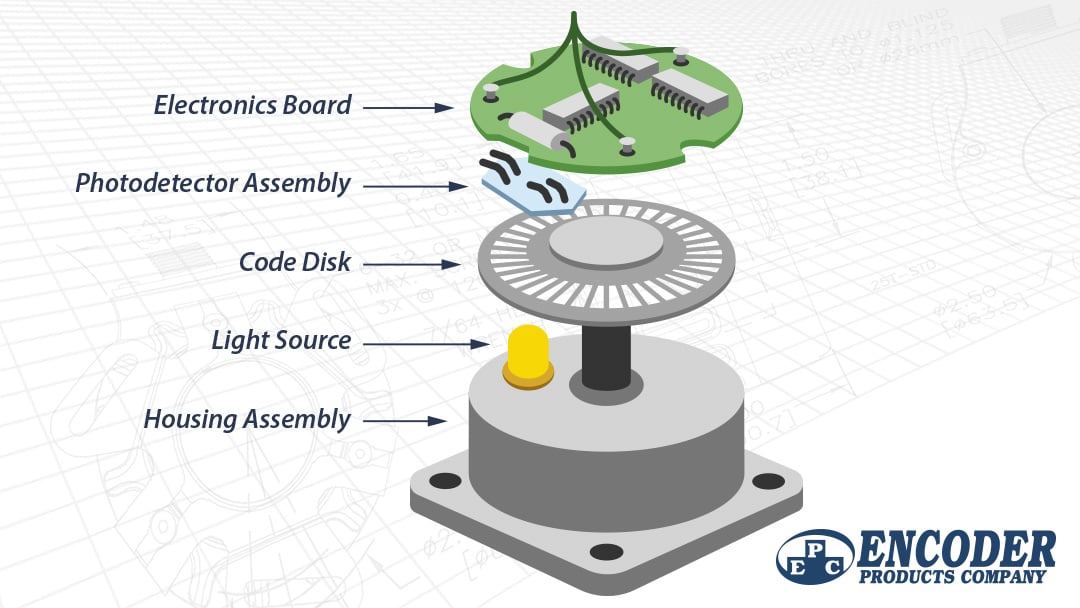
The graphic below outlines the basic construction of an optical incremental rotary encoder.
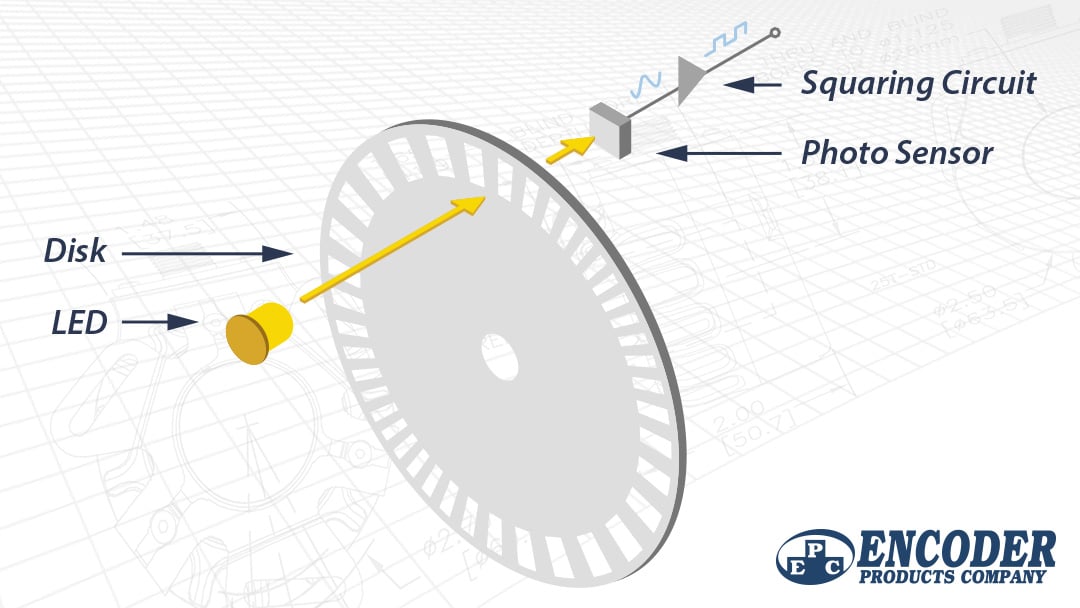
Broken down in steps, this is how an optical encoder provides motion feedback information:
- A beam of light emitted from an LED passes through a Code Disk, a transparent disk patterned with opaque lines (much like the spokes on a bike wheel).
- The light beam is picked up by a Photodetector Assembly, also called a photodiode array or a photosensor.
- The Photodetector Assembly responds to the light beam, producing a sinusoidal wave form, which is transformed into a square wave or pulse train.
- This pulse signal is simple:
light = on
no light = off
-
The pulse signal is then sent to the counter or controller through the Electronics Board.
- The counter or controller (not pictured) then sends the signal to produce the proper function (stop, go, rotate, etc.).
EPC sells a variety of optical incremental encoders, in both shaft and thru-bore/blind hollow bore packages. For help finding the right encoder for you application, contact us. When you call EPC, you talk to engineers and encoder experts who can help you specify the right encoder solution for your application.
For more information about how an encoder works, watch our Encoder 101 video, “What’s an Encoder?”